 响应式中的watch实现
响应式中的watch实现
# 概览
在vue3中,响应式数据的变化会触发watch和watchEffect中的参数函数,而二者都是基于reactivity包中的watch方法实现,其实现路径为packages\reactivity\src\watch.ts。这两个watch不是一回事。watch和watchEffect是基于本文的watch实现的,是vue3导出给用户使用的API接口,而本文中的watch是在reactivity中定义的,在整个vue3中,其命名为watch$1,vue3在packages\runtime-core\src\apiWatch.ts中引入了watch$1封装了一个doWatch方法,watch和watchEffect就是在doWatch上进一步封装实现的。
# 源码解析
watch的作用就是主动监听响应式数据source,当source发生变化时,便会触发cb函数,cb函数的参数就是响应式数据source的新值newValue和旧值oldValue,而第三个参数options就是一些配置项,决定了监听的方式、时机等。
# watch
watch的源码实现如下:
let activeWatcher= void 0;
function watch(source, cb, options = {}) {
// source : 可以是ref、reactive对象、数组或getter函数
// cb : 回调函数,source发生变化时被调用
const { immediate, deep, once, scheduler, augmentJob, call } = options;
/* immediate:是否立即执行回调
deep:是否深度监听
once:是否只执行一次
scheduler:调度函数,用于控制回调的执行时机
augmentJob:用于增强job函数
call:可选的调用函数,用于调用getter和cb
*/
const reactiveGetter = (source2) => {
if (deep) return source2;
if (isShallow(source2) || deep === false || deep === 0) {
return traverse(source2, 1)
}
return traverse(source2)
}
let effect; // 定义副作用
let getter; // getter函数
let cleanup; // 清理函数
let boundCleanup;
let forceTrigger = false; // 是否强制触发
let isMultiSource = false; // 是否包含多个监听对象
if (isRef(source)) {
// Ref处理
getter = () => source.value;
forceTrigger = isShallow(source); // 若是浅层响应,则强制触发,反之
} else if (isReactive(source)) {
// Reactive处理
getter = () => reactiveGetter(source); // 深度遍历控制
forceTrigger = true; // 强制触发
} else if (shared.isArray(source)) {
// 数组处理:遍历每项,处理各种类型
isMultiSource = true;
forceTrigger = source.some((s) => isReactive(s) || isShallow(s));
getter = () => source.map((s) => {
if (isRef(s)) {
return s.value;
} else if (isReactive(s)) {
return reactiveGetter(s);
} else if (shared.isFunction(s)) {
return call ? call(s, 2) : s()
}
})
} else if (shared.isFunction(source)) {
// 函数处理
if (cb) {
// watch 模式
getter = call ? () => call(source, 2) : source;
} else {
// watchEffect 模式
getter = () => {
// 执行上次清理
if (cleanup) {
pauseTracking();
try {
cleanup()
} finally {
resetTracking();
}
}
// 设置当前活跃watcher
const currentEffect = activeWatcher;
activeWatcher = effect;
try {
// 传入清理函数
return call ? call(source, 3, [boundCleanup]) : source(boundCleanup);
} finally {
activeWatcher = currentEffect;
}
}
}
} else {
getter = shared.NOOP;
}
// 深度监听处理:traverse函数会递归访问所有属性,确保收集完整依赖
if (cb && deep) {
const baseGetter = getter;
const depth = deep == true ? Infinity : deep;
getter = () => traverse(baseGetter(), depth);
}
// 获取当前副作用域
const scope = getCurrentScope();
// 定义watchHandle函数,用于清理副作用effect
const watchHandle = () => {
effect.stop();
if (scope && scope.active) {
shared.remove(scope.effects, effect);
}
}
// 若是一次性监听
if (once && cb) {
// 回调函数cb存在,则对cb进行二次封装
const _cb = cb;
cb = (...args) => {
//在cb执行完后,调用watchHandle清理副作用effect
_cb(...args);
watchHandle();
}
}
// 初始化 oldValue, INITIAL_WATCHER_VALUE实际上就是一个空对象
let oldValue = isMultiSource ? new Array(source.length).fill(INITIAL_WATCHER_VALUE) : INITIAL_WATCHER_VALUE;
// 核心调度任务 job
const job = (immediateFirstRun) => {
// immediateFirstRun 表示是否立即执行
if (!(effect.flags & 1) || !effect.dirty && !immediateFirstRun) {
return;
}
if (cb) {
// 执行回调,effect会返回新值
const newValue = effect.run();
// 变化检测,若deep或者强制触发为true,或者source的值发生变化,若是多源,只要其中一个值发生了变化,则都满足条件
if (deep || forceTrigger || (isMultiSource ? newValue.some((v, i) => shared.hasChanged(v, oldValue[i])) : shared.hasChanged(newValue, oldValue))) {
// 执行清理
if (cleanup) {
cleanup();
}
// 设置当前watcher上下文
const currentWatcher = activeWatcher;
activeWatcher = effect;
try {
// 构造回调参数
const args = [newValue, oldValue === INITIAL_WATCHER_VALUE ? void 0 : isMultiSource && oldValue[0] === INITIAL_WATCHER_VALUE ? [] : oldValue, boundCleanup]
oldValue = newValue;
// 执行回调
call ? call(cb, 3, args) : (cb(...args))
} finally {
activeWatcher = currentWatcher;
}
}
} else {
// watcherEffect模式直接运行
effect.run();
}
}
// 是否增强job
if (augmentJob) {
augmentJob(job)
}
// 定义副作用,实例化ReactiveEffect,参数为定义的getter函数,即对source进行参数归一化处理后的方法
effect = new ReactiveEffect(getter);
// 定义副作用的调度器,若配置项scheduler存在,则对job进行调度;否则调度器就是job
effect.scheduler = scheduler ? () => scheduler(job, false) : job;
//注册清理函数:清理函数在cleanupMap中维护
boundCleanup = (fn) => onWatcherCleanup(fn, false, effect);
cleanup = effect.onStop = () => {
const cleanups =cleanupMap.get(effect);
if(cleanups){
if(call){
call(cleanups,4)
}else{
for(const cleanup2 of cleanups) cleanup2()
}
cleanupMap.delete(effect)
}
}
// 若cb回调函数存在
if (cb) {
if (immediate) {
// 若是立即执行,则调用job方法,该方法会执行cb回调
job(true);
} else {
// 若不是立即执行,则调用effect.run,获取旧值oldValue
oldValue = effect.run();
}
// 若存在调度器配置项
} else if (scheduler) {
// 则执行调度器方法,传入job
scheduler(job.bind(null, true), true)
} else {
// 否则运行effect.run
effect.run();
}
// 定义 watcherHandle的暂停/恢复/停止方法,暂停和恢复就是对effect状态的一个控制
watchHandle.pause = effect.pause.bind(effect);
watchHandle.resume = effect.resume.bind(effect);
watchHandle.stop = watchHandle;
// 最后返回watcherHandle
return watchHandle;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
vue3中定义了一个全局的activeWatcher,可以调用getCurrentWatcher获取当前激活的watcher;watcher方法内部就是对监听对象source进行了参数归一化的处理,由此得到一个getter函数,然后通过将getter参数传给,ReactiveEffect实例化一个副作用effect,当执行effect.run时就会运行getter,由此完成对响应式的依赖进行收集,当这些响应式数据发生变化时,就会触发在watch方法中定义的effect副作用这个依赖,即会触发effect.trigger方法,进而触发其调度器,而watcher中定义的job就会在该调度器中运行,进而执行回调函数cb.
# watcher的流程处理
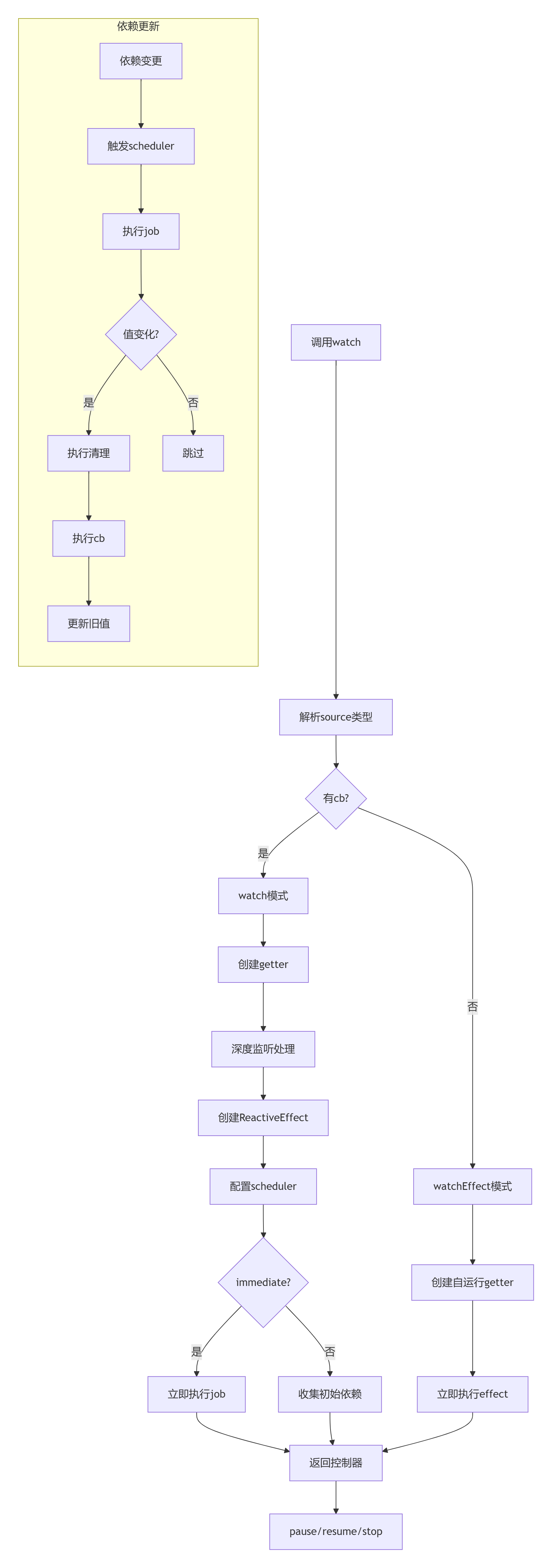
# 辅助方法
watch的辅助方法包括onWatcherCleanup和traverse。
# onWatcherCleanup
vue3定义了一个全局的cleanupMap,该对象中会存储注册清理函数,该清理函数可以右用户自定义,其实现如下:
const cleanupMap = new WeakMap();
function onWatcherCleanup(cleanupFn, failSilently = false, owner = activeWatcher) {
if (owner) {
let cleanups = cleanupMap.get(owner);
if (!cleanups) cleanupMap.set(owner, cleanups = []);
cleanups.push(cleanupFn);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# traverse
traverse方法就是对响应式对象value进行深度递归遍历。
function traverse(value, depth = Infinity, seen) {
// 若depth小于1 或者 value不是一个对象,或者value的__v_skip属性为true,则返回value
if (depth <= 0 || !shared.isObject(value) || value('__v_skip')) {
return value;
}
seen = seen || new Set(); // 定义一个 Set
if(seen.has(value)){ // 若seen存在value,则返回value
return value
}
seen.add(value); // 向seen中添加value
depth--; // 深度自减
// 对value的各类型进行判断,以及递归处理
if (isRef(value)) {
traverse(value.value, depth, seen)
} else if (shared.isArray(value)) {
for (let i = 0; i < value.length; i++) {
traverse(value[i], depth, seen);
}
} else if (shared.isSet(value) || shared.isMap(value)) {
value.forEach((v) => {
traverse(v, depth, seen)
})
} else if (shared.isPlainObject(value)) {
for (const key in value) {
traverse(value[key], depth, seen)
}
for (const key of Object.getOwnPropertySymbols(value)) {
if (Object.prototype.propertyIsEnumerable.call(value, key)) {
traverse(value[key], depth, seen)
}
}
}
// 最后返回value;
return value
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
